A microscope is an examining tool used in laboratories to examine and evaluate an object that we cannot see with our naked eye. Sometimes, the things we want to focus on are so tiny that they are not visible to our eyes. So, we have to take help from a microscope for seeing those objects, and it helps us in further investigations related to that object.
As I mentioned above, there are various types of microscopes available in the market, and in this article, we’ll try to sum them up into five leading types to help you with the subject. I’ll try my best to keep the wording accessible and understandable to develop a complete insightful understanding of the said topic.
So, let’s get started with the list of several types of microscopes, but before that, take a brief look at the parts and functions of microscopes.
Table of Content:
- 5 Different Kinds of Microscopes
- 5 Types of Microscopes Comparison Chart
- 16 Parts of a Microscope and their Functions
- 2 Types of Electron Microscopes
- 4 Types of Light Microscopes
5 Different Kinds of Microscopes
This article will tell you about the five most used and popular microscopes. Moreover, what are the importance of using different types of microscope. You’ll get to know the answer to this question as well. Other jobs require various kinds of Microscopes.
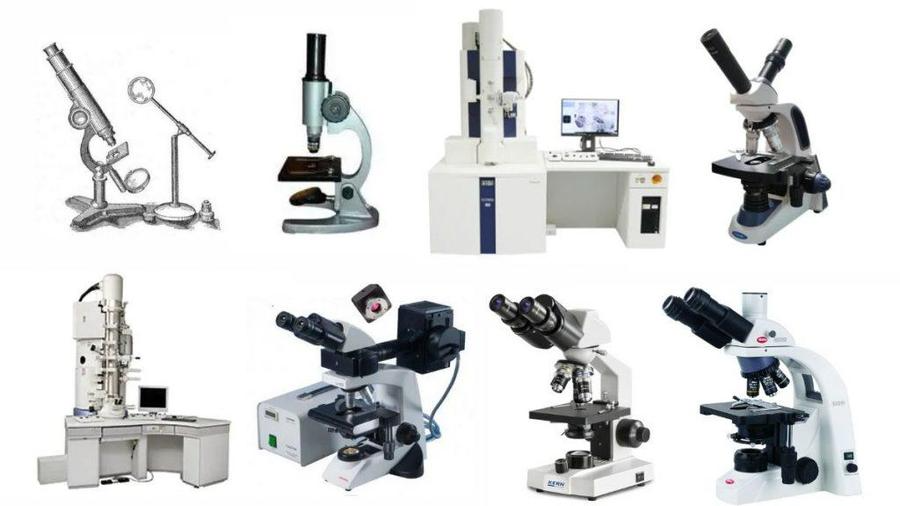

By the time you go down, you’ll come to know about microscopes that can be used to view live cells, types of electron microscopes, types of light microscopes, and the list of various kinds of microscopes. So, let’s get started.
Latest Blog: Guidelines for Sight Adjustment & MIL vs MOA Which one is Better
1) Compound Microscopes
A compound microscope has another name, and that is a biological microscope. Types of microscopy are a vast subject to discuss, and each one has a particular job to perform. The compound microscope is used in schools, laboratories, veterinary labs, pathology, histology, and wastewater treatment plants. The microscope slide is used to examine the samples, and a coverslip helps flatten the object on the stage.
There are several samples that you can examine with the help of a compound microscope. If you go for an open search for about ten different types of microscope, the compound microscope will undoubtedly lead to the results from the front. It is because of its significance and variety of usage.
The list of samples that you can evaluate includes cheek cells, blood cells, bacteria, parasites, thin sections, tissues, and more. You can examine all these samples with a compound microscope super quickly. And let me mention it here, you cannot see these objects with your naked eye, so this scope helps you see them.
So, it was all about compound microscopes, and the other four types of Microscopes are explained below. The magnification of this microscope may vary, and it comes like, 40x, 100x, 400x, and it can also go up to 1000x.
But, it would help if you were careful while purchasing a microscope with 1000x; most of the time, they are not up to the mark, resolution, and quality of the image are not so good. If you are unaware of what microscope can see cells, the answer is a compound microscope.
Read Also: Different Types of Rifle Scopes
2) Stereo Microscope
The stereo microscopes are so good for observing and examining objects that you can hold in your hands, and it usually has magnification between 10x to 40x. It provides you 3D images and stereo images.
It has a range of jobs to perform and various samples you can examine on this microscope, such as botany samples, flowers, coins, plastic, insects, printed circuit boards, frog anatomy, fabric weaves metal parts, and more.
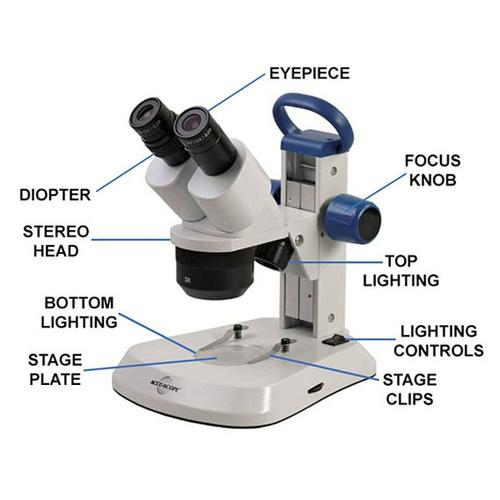

You can use it at different offices, such as manufacturing units, high school dissection, science, and coin collecting. If you look at microscope images, stereo images are the best. If you are not aware of 3D microscope names, you need to try a stereo microscope once, and you’ll find it worth using. If you explore types of microscopes comparison charts, each one has a unique set of uses, functions, and parts.
The stereo is all good to use for several things you can see with your naked eye but cannot observe the little articles within those objects. It shows everything clear, and you can increase or decrease magnification to make the image clear and precise.
3) Metallurgical Microscope
Many objects do not allow light to pass through their bodies, and it becomes so difficult to examine them thoroughly. For those objects, we use a metallurgical microscope. The metallurgical microscopes are also handy for reading metals, thin paints, and grain sizing.
These objects do not let any light pass through them, and if there is any crack in these objects, that can cause issues to the infrastructure you are using them in. This metallurgical microscope can fully make it up to your expectations to prevent such problems as cracks, break, and flings.
It is one of the most popular Microscopes, and the metal production units and paint industries use it immensely.To know more about microscopes and their uses, read the article to the last word. The magnification of these microscopes varies with 50x 100x, 200x, and sometimes 500x. You can set it at any level as you need it.
4) Inverted Microscope
These microscopes are available in metallurgical inverted and biological inverted microscopes. It also comes with different magnification powers such as 40x, 100x, 200x, and 400x. You have to place a Petri dish on the stage to observe the samples of living objects.
These microscopes are used in various offices, fields such as live-cell imaging, microbiology, neuroscience, and developmental biology. These optical microscopes are the best way to examine all these living samples. It is one of the best types of microscopes in biology.
The Petri dish is used in inverted biological microscopes. On the other hand, the inverted metallurgical microscope has no med for the Petri dish, and all you need to do is place the flat sample on the stage. If you want to understand all the different kinds of microscopes, you are near to making it up.
5) Polarizing Microscope
The polarizing microscope is the beat to examine the rocks, minerals, and chemicals. There is a wide usage of this microscope, and many professionals use it in the field, such as chemists, petrologists, geologists, and pharmaceutical industries, use it daily.
The polarizer kinds of microscopes have two significant aspects, and each one has a unique function to perform. The polarizer allows the microscopes to pass the light through it, and the analyzer deals with the right amount of light, its direction towards the illuminated samples. I hope now you are very much aware of the types of microscopes and their usages.

All the types of Microscopes that we explained above are super good but do not overlap with the functionality. If you read about some authentic types of microscope pdf on the internet, I hope you’ll not find any dissimilarity with the information I shared in this article.
The types of the microscope in microbiology, biology, geology, lab work, and other complex objects related to examination that you cannot do with your naked eye, these five microscopes can do it with super ease seamlessly.
5 Types of Microscopes Comparison Chart
In this section, I’ll tell you all the major dos and don’ts of different types of microscopes. So, let’s not waste time, and head towards the types of microscopes comparison chart below.
| Compound microscope | Stereo microscope | TEM Electron | SEM Scanning | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Living sample | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| 2D/3D image | 2D, sometimes 3D with living things | 3D | 2D | 3D |
| Allow you to see inside the cell or Surface? | Inside | Surface | Inside | Surface |
| Type of magnification | 40x, 100x, 400x, and up to 2000x | 10x, 30x, 40x | Up to 2,00,000x | Usually, 1500000, can go up to 50, 000, 000 |
| Examples of Livings things that can be examined | Bacteria, animals, plants, fungi cells, membrane, nucleus, cell wall, etc. | Worms, leaves, insects, the inside of fruits, hands, fingers, mushrooms, etc. | The surface of insects, animals, pollen grain, etcInside of cell for detail, cell organelles, high resolution and magnification |
16 Parts of a Microscope and their Functions
There are multiple microscope types, parts, and functions of microscopes. In this manual, we’ll uncover all the secrets behind it and answer all your microscope questions. In this part, I’ll explain the whole of the microscope in 16 details. Each part has a job to perform in the overall performance of the microscope. Microscope parts and functions are easy to understand, so let’s begin the show with the first component.
1) Base
It performs the job of a support system for the microscope based on its name. It gives support to the device’s overall upper and lower body, and it also helps carry illuminators.
2) Head:
Different types of Microscopes have different kinds of components. The head component is one of the critical parts, and it manages the upper body, and all the optical components come under the zone of the head. It is also called the body of the microscope.
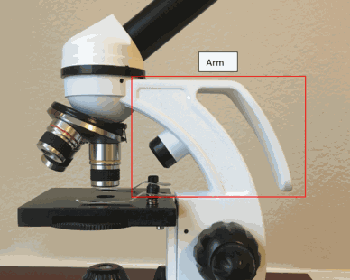
3) Arms:
The arms are so handy to place a microscope or move it from one folate to another. It is the part that holds upper and lower parts together and keeps them aligned as you need them to use for microscopy.
The middle part usually comes in a curved shape to hole the upper optical components and enable you to focus on the object.
4) Eyepiece:
The eyepiece is an inevitable part of the microscope, and it comes at the top of the instrument. The point from where you look through the microscope to observe and examine your object is called eyepiece; it has another name that goes like Ocular.
So, it enables you to look and keep the thing through the scope. Usually, it comes with 10x magnification, but you can change it as the situation demands between 5 to 40x.
5) Eyepiece Tube:
The tube holds the eyepiece and helps you monitor the object as you want. You can change its placement bit; not eyepiece tubes offer the same. In binos, you get a flexible eyepiece tube for customization, while in monoculars, you get a fixed and nonflexible eyepiece tube. It varies with the types of Microscopes.
6) Nose Piece:
It is a rotating turret that holds the objective lens. It can also revolve the objective lens as the magnification settings demand if we look at its moveable structure.
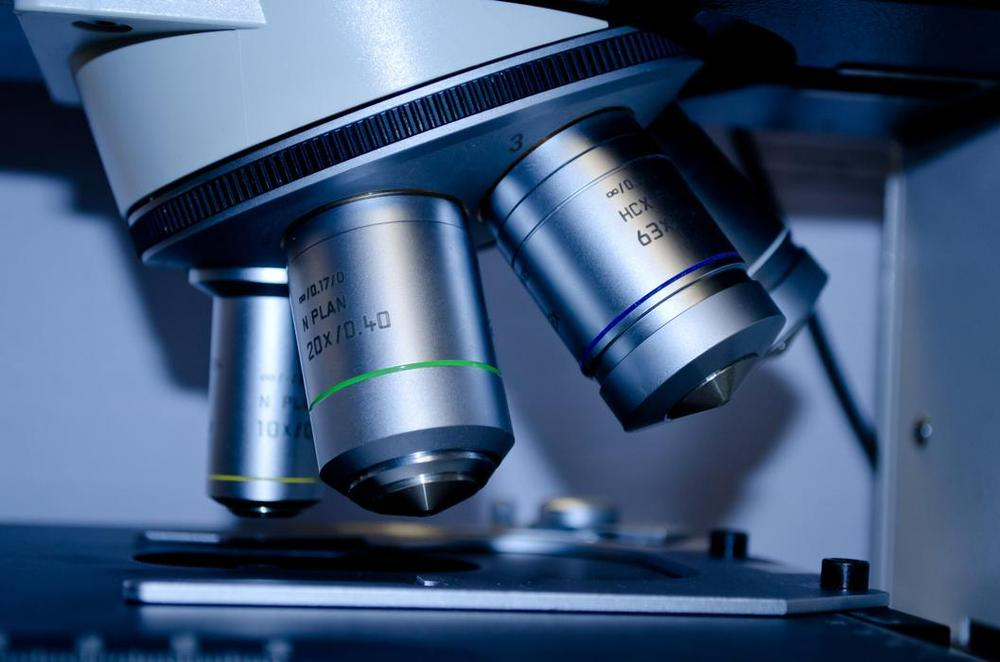

7) Objective Lenses:
Different four objective lenses come with a microscope, and each one has a different power set of magnification. Usually, the magnification goes around 40x to 100x, and you can set it at any level you feel good about it.
It helps your vision to have a zoom-in shot of the object. Different types of Microscopes carry various sizes of objective lenses and magnification powers.
8) The Adjustment Knob:
There are usually two types of knobs that come with a microscope, one is a coarse adjustment knob, and the other is a fine adjustment king. These are so helpful in controlling the functions of microscopes and all the changes you can make by using these two.
9) Stage:
The stage is a clip where you place your specimen object to examine thoroughly. There are various types of stages that you can have, but the mechanical stage is the handiest one. It eliminates the manual work and can move the slides of objects themselves. So, it has a vital function to perform in microscopy.
10) Condenser:
Near the diaphragm, the consensus takes place. It is a part that collects and transmits the light to the specimen you put on the stage. These are lenses, and it gets light from the illuminator for the specimen. Without having this component, you cannot throw any light on the specimen.
It helps immensely in the process to produce pictures with 400x magnification power. So, the more you get the magnification power of the condition, the higher the clarity and precision of the image will be.
11) Diaphragm:
It is a multi-tasking component that locates on the stage, and its primary job is to control light and help it reach the specimen. It has a variety of options with lower and more power. If you want a powerful microscope, it comes with an Abbe condenser. So types of Microscopes are the main decider behind these components.

12) Condenser Focus Knob:
The condenser controls the light on the specimen, and to maintain that condenser; there is a focus knob that you can use; it is called the condenser focus knob. It helps you immensely in the process by allowing you to live the consensus up or down.
13) Abbe Condenser
It is the super condenser that controls more magnification. It is designed for making an ordinary microscope a luxurious one. It is used in the highest quality and powerful microscopes. You can enjoy up to 400x magnification by using an abbe condenser. It depends on the types of Microscopes, whether you should use abbe consensus or the simple condenser.
14) Aperture:
Aperture is a tiny hole on the stage that is the only way to transmit the light to make it reach the specimen. It is such a handy tool.
15) Microscopic Illuminator:
It works as a mirror and is located in the base. It can collect light from external sources but with a low voltage of up to 100V. It gathers light for further transmission of the same to the stage.
16) The Rack Stop:
As its name tells, it stops and controls the stage to go too much closer to the specimen, which may cause damage to the specimen slide. The barrier between the objective lens and the specimen slides made sure both were at a considerable distance.
2 Types of Electron Microscopes
It is a type of microscope that uses a beam of electrons and their waves to magnify an object on the stage. On the other hand, the light microscope does the opposite and uses visible light to magnify the image. So, you can say these two share a major difference in lighting systems: one has a beam of electrons and the other one has a visible light system. Let’s take a look at the subtypes of electron microscopes.
1) Scanning Electron Microscope
In a scanning electron microscope, a beam of electrons performs the main job and it scans one surface of the object, where the specimen lies within the stage. After scanning, it uses input and projects it in the form of an image to the user.
2) Transmission Electron Microscope
The transmission electron microscope helps you observe thin objects such as molecules, tissues, and other specimens. The electron passes through these specimens and projects an image to give you a view of the sample in a clear manner.
4 Types of Light Microscopes
It is an opposite system to the electron microscope. In a light microscope, a system of visible light is used. It has multiple lenses to perform the job of generating an image to look through the eyepiece. There are four subtypes of light microscopes which are explained below.
1) Phase Contrast Light Microscope
While the light is penetrating through the uncolored sample, the deviation of a small amount of light is known as phase shift. These phase shifts convert the scenario into a whole colorful picture. When the light passes through that unstained specimen, it illuminates and creates a bright image in the background that you can see through the eyepiece.
2) Bright Field Light Microscope
It is the microscope that is mostly used in microbiology labs and it provides a dark image with a bright background. That is why it is called a bright field light microscope. You can examine animal cells and plant cells through it and it uses a couple of lenses to do this job.
3) Fluorescence Light Microscope
In all other three types of light microscopes, you get to see an image after the light passes through the objects but not in this one. In this case, the specimen itself emits lights. A dye molecule that you add with the specimen, absorbs light energy. This dye molecule is a fluorochrome, so at a specific wavelength, it emits light and causes it to create an image.
4) Dark Field Light Microscope
It is very similar to the phase-contrast microscope. In this microscope, a condenser that creates a hollow beam of light, with the help of placement of a dark field stop, enters the object. This system helps you visualize the living objects which are colorless and unstained. When illumination is done and the light passes through that uncolored sample, it creates an image to examine the object with clarity.
So, this was a comparison chart of various types of microscopes. I tried to keep it simple and understandable for beginners. Not all microscopes are good to observe and examine living objects, not all for dead ones.
So, before you buy a microscope for yourself, you need to ensure whether you need it to examine dead or living objects. After this phase, you can get help from the information shared in this article to make a rational purchase decision.
After reading this article, I hope you must be fully aware of all the types of Microscopes. Whether you want to purchase a microscope to use in the lab, office, production unit, or any other field that you are not sure about with your naked eye, all these microscopes can help you extensively with your purposes.
I have used multiple microscopes for years and know much about their usage, functions, and outlines. So, this article is the conclusion of all those years’ experience.
Conclusion:
Different types of microscopes give you the freedom of enjoying various magnification without lowering the quality of images. When you intend to buy a microscope, you need to be very clear about which purpose you want one. There are a couple of things such as an accurate eyepiece with multiple magnification powers to utilize, you need to focus on these aspects to get the finest device to use.
The light microscope is the best device to see cells. It has all the technical details that help you examine the cells, and their structures. You can magnify the specimen about a thousand times to get the ultimate clear view. You can use multiple built-in lenses to observe the samples with the utmost precision and accuracy.
When it comes to optical microscopes, there is no rocket science to understand it in less than a minute now. Because the optical microscopes are the same as we discussed above. Light microscopes are also called optical microscopes. So, it is called buy one get one free, the best reading deal.